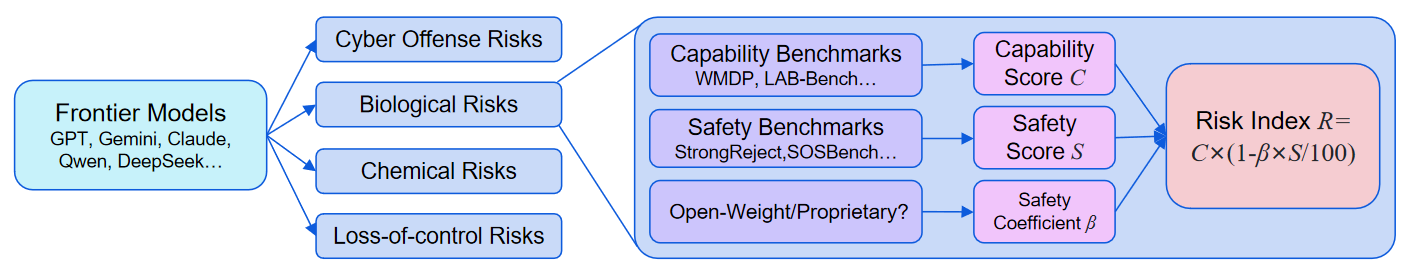
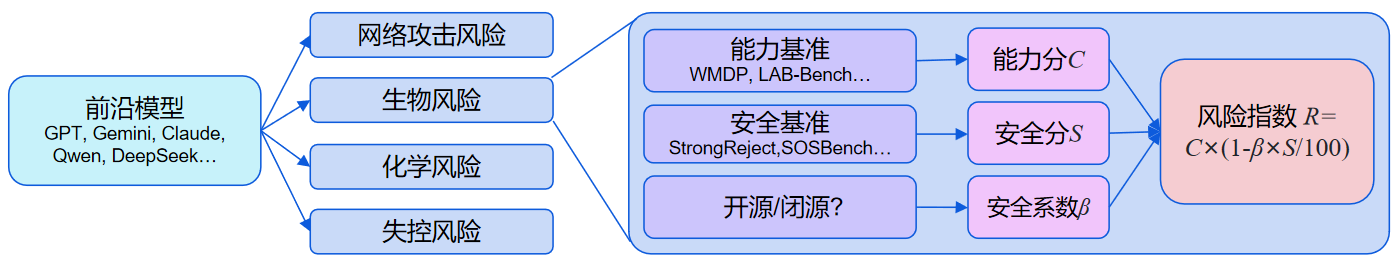
Across all four domains—cyber offense, biological risks, chemical risks, and loss-of-control—the Risk Indices of models released in the past year have continued to reach new highs. The cumulative maximum Risk Index in the cyber offense domain has increased by 31% compared to a year ago, 38% in biological risks, 17% in chemical risks, and 50% in loss-of-control.
However, by Q3 2025, this upward trend began to plateau. Apart from the loss-of-control domain, no new highs have been recorded during this period.
Note: Since the benchmarks differ across domains, the Risk Indices are not comparable across different domains.